Obesity and Cancer: Is there a link?
So, what is obesity?
It’s excess body weight in terms of fat mass. Obesity is a growing problem in our society today, due to the rapid adoption of a modernized lifestyle that results in increased carbohydrate intake, reduced physical activity and hectic schedule in our lives among many others.
Causes of obesity:
Obesity is not just about food and there can be more than one cause. To mention a few of lifestyle factors-
● Psychological factors- stress and other concerns like sleep deprivation, over a long period of time.
● Positive energy balance- When your energy intake is greater than your energy output. One of the reasons being, lack of physical activity or leading a sedentary lifestyle. That means that you are eating more calories than your body needs which leads to storage of excess energy in the form of fat.
● Hormonal issues- like PCOS, insulin resistance etc.
● Culture and environmental- wrong marketing of the products, traditions and culture that promote eating unhealthy foods on a regular basis, not enough access to fresh and healthy food etc.
Is there a link between obesity and cancer?
Yes, absolutely! Various studies show that excess body fat increases your risk for several cancers, including colorectal, post-menopausal breast, uterine, esophageal, kidney and pancreatic cancers.
How?
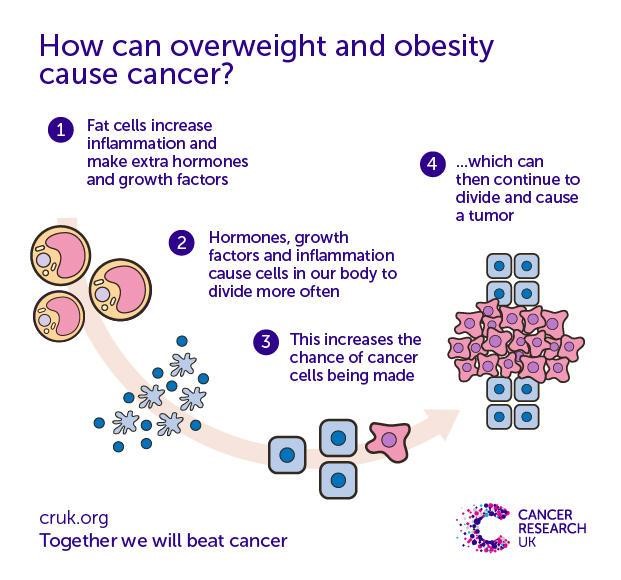
Experts believe it’s largely due to the inflammation caused by visceral fat – the fat that surrounds your vital organs. Being overweight and obese over a long duration of time can affect certain changes in our body. These changes can include long-lasting inflammation and higher than normal levels of insulin, insulin-like growth factor and sex hormones.
How does obesity cause inflammation/ insulin resistance?
According to NCBI, obesity is the accumulation of abnormal or excessive fat that may interfere with the maintenance of an optimal state of health. The excess of macronutrients in the adipose tissues stimulates them to release inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 6, and reduces production of adiponectin, predisposing to a pro-inflammatory state and oxidative stress. The increased level of interleukin 6 stimulates the liver to synthesize and secrete C-reactive protein which is considered as the marker of inflammation in our body. Long-term inflammation caused by excess visceral fat, however, can damage your body and increase your risk for cancer. Cancer happens when cells reproduce uncontrollably, damaging the cells around them and causing illness. The more cells divide and reproduce, the higher the risk that something will go wrong and a tumor will form.
Inflammation caused by obesity can keep the body from properly responding to insulin. This is called insulin resistance. When the body doesn’t respond to insulin correctly, it produces more insulin to make up for that. The increase in insulin due to insulin resistance triggers an increase in the number of cells produced, which can lead to cancer. Increased insulin also affects how hormones like estrogen are controlled. More insulin can lead to more available estrogen, which increases cancer risk.
Furthermore, it also promotes the growth of IGF‐1 which is known to promote cancer development by inhibiting apoptosis and stimulating cell proliferation. Epidemiological studies have reported a positive association between circulating IGF‐1 levels and various primary cancers, such as breast, colorectal and prostate cancer.
How does excess body fat cause estrogen imbalance?
After menopause, fat cells produce the hormone estrogen. This can make cells in the breast and womb divide more often which increases the risk of cancer developing. In women, too much estrogen is linked to an increased risk for post-menopausal breast, endometrial and ovarian cancers.
Will you definitely get cancer if you are obese?
Being overweight or obese doesn’t mean that you’ll definitely develop cancer, however if you are overweight or obese, your risk of developing cancer is higher.
So, what can we do about it?
● Speak to your nutritionist or a dietitian and start maintaining a healthy diet. Make sure that you eat at least 3-4 cups of fresh, seasonal, low glycemic index fruits and vegetables every day. Research shows that a diet rich in fruits and veggies helps in reducing the risk of developing cancer. They also help in reducing inflammation.
● Choose healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fish, avocado and walnuts, other nuts and seeds. These foods are also considered anti-inflammatory.
● Select proteins such as fish, grass fed lean meats, eggs, nuts, seeds, lentils and legumes.
● Opt for healthy sources of carbohydrates, such as organic whole grains, legumes, and fruits and vegetables and make sure you keep this to a minimum, as we Indians tend to binge eat the same.
● Keep yourself well hydrated.
● Stay active. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity a week.
● Sleep well and rest well.
Reference:
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/obesity/obesity-fact-sheet
https://www.mdanderson.org/publications/focused-on-health/how-does-obesity-cause-cancer.h27Z1591413.html
https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/obesity-weight-and-cancer/does-obesity-cause-cancer
Tags: Obesity, excess body weight, fat mass, modernized lifestyle, increased carbohydrate intake, reduced physical activity, and hectic schedule, Causes of obesity, Psychological factors, Positive energy balance, lack of physical activity, sedentary lifestyle, Hormonal issues, PCOS, insulin resistance, Culture and environmental, inflammation, visceral fat, long-lasting inflammation, insulin-like growth factor, sex hormones, tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 6, adiponectin, C-reactive protein, IGF, reducing inflammation, omega-3 fatty acids, stay active, cancer